What is bulletproof glass?
Bulletproof glass is a special multilayered material designed to withstand impact from firearms and explosive devices. Its structure includes several layers of glass and polymer materials that absorb the kinetic energy of a bullet and prevent it from penetrating. Thanks to this composition, bulletproof glass not only stops bullets but also reduces the risk of dangerous glass shards forming.
History of Bulletproof Glass: When and Who Invented It
Bullet-resistant glass first appeared in the early 20th century. In 1903, French chemist Édouard Bénédictus accidentally discovered the strengthening effect of glass when combined with a cellulose film. This discovery later became the basis for laminated glass technology.
By 1918, the French army began using bullet-resistant glass to protect drivers of military vehicles. With the advancement of technology, more sophisticated multilayer designs were developed that provided protection not only from bullets but also from explosions.
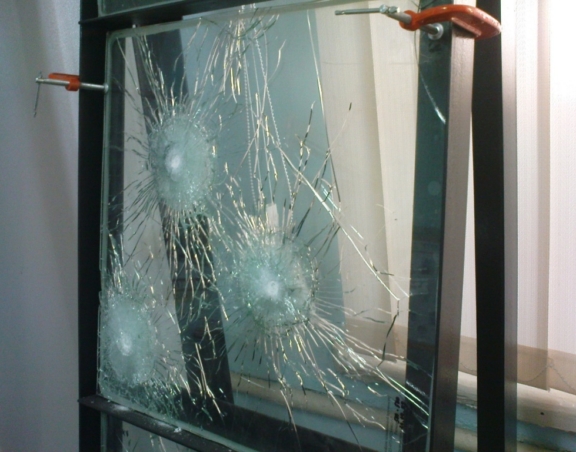

Where is Bulletproof Glass Used?
Bulletproof glass is widely used in various fields where enhanced protection against firearms and explosives is necessary. It plays a key role in ensuring safety in environments where there is a threat of armed attacks, explosions, or other acts of violence. Due to its strength, ability to stop bullets, and minimize fragmentation, this material is commonly used in military, civil, commercial, and government infrastructure.
Main Areas of Application for Bulletproof Glass
Bulletproof glass is an essential part of security systems across numerous sectors — from military and law enforcement to commercial and civilian infrastructure. Its use allows for the effective protection of human life, property, and critical assets against a wide range of threats.
International Classification of Bulletproof Glass
European Classification (EN 1063)
In the European Union, the classification of bullet-resistant glass is regulated by the EN 1063 standard. This system categorizes glass into BR (Ballistic Resistance) classes based on the type of firearm it can withstand.
| Class | Weapon | Caliber | Bullet Energy (J) | Number of Shots |
| BR1 | Pistol | .22 LR | 168 | 3 |
| BR2 | Pistol | 9 mm Luger | 518 | 3 |
| BR3 | Pistol | .357 Magnum | 857 | 3 |
| BR4 | Pistol | .44 Magnum | 1518 | 3 |
| BR5 | Rifle | 5.56×45 mm NATO | 1795 | 3 |
| BR6 | Rifle | 7.62×51 mm NATO | 3291 | 3 |
| BR7 | Rifle | 7.62×51 mm NATO (armor-piercing) | 3510 | 3 |
American Classification (UL 752)
In the United States, bullet-resistant glass is classified according to the UL 752 standard. It defines 10 levels of protection, ranging from handguns to high-caliber weaponry.
| Level | Weapon | Caliber |
| Level 1 | Pistol | 9 mm |
| Level 2 | Pistol | .357 Magnum |
| Level 3 | Pistol | .44 Magnum |
| Level 4 | Rifle | .30-06 |
| Level 5 | Assault Rifle | 7.62×39 mm |
| Level 6 | Pistol | 9 mm (enhanced protection) |
| Level 7 | Rifle | 5.56×45 mm NATO |
| Level 8 | Rifle | 7.62×51 mm NATO |
| Level 9 | Rifle | 12.7×99 mm (.50 BMG) |
| Level 10 | High-Caliber Artillery | 20 mm |
NIJ 0108.01 Standard
In addition, the United States uses the NIJ 0108.01 standard, developed by the National Institute of Justice.
| Level | Weapon Type | Caliber | Bullet Type |
| Level I | Pistol | .22 LR and .380 ACP | Standard bullets |
| Level II-A | Pistol | 9 mm and .40 S&W | Standard bullets (low velocity) |
| Level II | Pistol | 9 mm and .357 Magnum | Standard bullets |
| Level III-A | Pistol | .44 Magnum and 9 mm | High-velocity bullets |
| Level III | Rifle | 7.62×51 mm NATO (.308) | Full Metal Jacket (FMJ) |
| Level IV | Rifle | .30-06 | Armor-Piercing (AP) bullet |
This standard is used in law enforcement and military applications and classifies the bullet resistance of materials based on weapon type and bullet caliber.
It includes protection levels ranging from light handgun threats to armor-piercing ammunition used in military operations.
Bulletproof Glass Strength Classes in Ukraine (DSTU 4546:2006)
| Resistance Class | Projectile Type | Bullet Description | Bullet Mass (g) | Test Distance (m) | Bullet Velocity (m/s) | Barrier Thickness (mm) | Number of Shots | Weapon |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RC 1 | 9 mm pistol cartridge 57-N-181s | Round-nose bullet with a steel core and steel jacket | 5.9 | 5.0±0.5 | 315±10 | 125±10 | 3 | Makarov pistol (PM), Stechkin automatic pistol (APS), ballistic barrel |
| RC 2 | 7.62 mm pistol cartridge 57-N-134s | Round-nose bullet with a steel core and steel jacket | 5.5 | 5.0±0.5 | 430±15 | 125±10 | 3 | Tokarev pistol (TT), ballistic barrel |
| RC 3 | 7.62 mm cartridge 57-N-231 (1943 model) | Pointed bullet with steel core and steel jacket | 7.9 | 10.0±0.5 | 730±15 | 125±20 | 3 | AK-47, AKM, Simonov SKS carbine, RPK light machine gun, ballistic barrel S-43 |
| 5.45 mm cartridge 7N6 | Pointed bullet with steel core and steel jacket | 3.4 | 10.0±0.5 | 910±15 | 125±20 | 3 | AK-74, RPK-74 light machine gun, ballistic barrel S-13VR | |
| RC 4 | 5.45 mm cartridge 7N10 | Pointed bullet with hardened steel core and steel jacket | 3.6 | 10.0±0.5 | 910±15 | 125±20 | 3 | AK-74, RPK-74 light machine gun, ballistic barrel S-13VR |
| 7.62 mm rifle cartridge 57-N-323s | Pointed bullet with steel core and steel jacket | 9.6 | 10.0±0.5 | 850±15 | 125±20 | 3 | SVD rifle, PK/PKT machine gun, ballistic barrel S-08 | |
| RC 5 | 7.62 mm armor-piercing incendiary (API) cartridge | Pointed bullet with hardened steel core and steel jacket | 7.4 | 10.0±0.5 | 745±15 | 125±20 | 3 | AK-47, AKM, Simonov SKS carbine, RPK, ballistic barrel S-43 |
| RC 6 | 7.62 mm B-32 rifle cartridge | Pointed bullet with hardened steel core and steel jacket | 10.4 | 10.0±0.5 | 830±15 | 125±20 | 3 | SVD rifle, PK/PKT machine gun, ballistic barrel S-08 |
Regulatory Framework in Ukraine
Key documents regulating the quality and classification of bulletproof glass include:
- DSTU 4546:2006 – multilayer protective glass
- GOST 30826-2014 – bullet-resistant glass
- ISO 16935 – international testing standards
How Bulletproof Glass Is Tested: Quality Assurance Procedures
Bullet-resistant glass is used in sectors where safety is critically important. Therefore, it undergoes thorough testing before being put into use.
The main goal of testing is to determine whether the glass meets the declared protection class and whether it can withstand bullet impacts of various calibers without penetration.
🔸 Ballistic Testing
This is the most important test and is carried out according to international standards (EN 1063, UL 752, NIJ 0108.01, DSTU 4546:2006).
During the test, the glass is fired upon using standard firearms of a specific caliber. The following factors are considered:
- Number of shots
- Firing distance (typically 5 to 10 meters)
- Bullet impact angle (usually 90°)
- Whether full penetration or hazardous fragmentation occurred
Rigorous testing ensures that the bulletproof glass complies with international safety standards and can reliably protect people and assets from ballistic threats.
These tests also help manufacturers improve their products, making them even more secure and efficient.
What Customers Should Know Before Ordering Bulletproof Glass
✅ Define the required protection level
✅ Specify the dimensions and shape of the glass
✅ Consider the operational conditions
✅ Review the manufacturer’s certifications and documentation
Price of Bulletproof Glass: How Much Does It Cost?
The price of bulletproof glass is determined by several key factors, including the protection class, thickness, dimensions, and the materials used.
We manufacture bullet-resistant glass that meets various durability standards — from basic protection levels to glass capable of withstanding fire from automatic weapons.
Depending on your specific requirements, we design the optimal construction, which directly affects the final price.
It’s important to understand that the cost of such products is not fixed, as there are no universal solutions in the field of protective glass manufacturing.
Each order is calculated individually, taking into account the conditions of use, the type of weapon the glass must withstand, and any additional features, such as:
- Tinting
- Anti-shatter film
- Reinforced polymer layers
The cost of bulletproof glass in Ukraine also depends on the manufacturing technology.
For example, glass with polymer inserts is lighter than traditional multilayer constructions, which simplifies installation while still providing a high level of protection and reliability.
If you’re wondering how much bulletproof glass costs, we’re ready to provide a detailed quote based on your specific needs.
Just leave a request on our website or contact us by any convenient means — and our experts will select the best solution for your budget and required level of protection.

Certification and Compliance Documents
Bulletproof glass is a crucial element of modern security systems, and its effectiveness must be confirmed through proper testing and certification.
International and national standards are used to assess protection levels, test methods, classifications, and production requirements.
🔸 Bulletproof Glass Certification Process
Certification involves several stages:
- Laboratory testing — the glass is tested for compliance with applicable standards.
- Conformity assessment — analysis of the material’s properties, structure, and manufacturing process.
- Issuance of certificate — upon successful completion, an official document is issued confirming the protection class of the glass.
🔸 Documents That Confirm Protection Level
After successful testing, the manufacturer receives a complete set of certification documents:
- Test report — an official document with the results of ballistic testing.
- Certificate of conformity — confirms that the product meets the requirements of a specific standard.
- Technical data sheet — includes product specifications and recommendations for installation and use.
Certification is a mandatory process that ensures compliance with international safety standards.
Having valid certificates and test reports confirms the glass’s ability to withstand threats and guarantees reliable protection of the facilities where it is used.
Heated Bulletproof Glass: Protection and Comfort in One Solution
Heated bulletproof glass is an innovative solution that combines high ballistic resistance with integrated heating capability.
This technology is used in military vehicles, armored cars, banks, government buildings, and even in residential properties with high security demands.
Construction and Functionality
This type of glass consists of multiple layers, including:
- Safety glass
- Polymer interlayers (such as EVA or PVB)
- Polycarbonate sheets for additional strength
A heating film or conductive mesh is embedded inside the structure to evenly distribute heat across the surface.
The heating is powered by electricity, which allows the system to:
- Prevent fogging and icing
- Maintain visibility in all weather conditions
- Provide comfort inside armored vehicles or protected areas
This combination of protection and comfort makes heated bulletproof glass a smart and advanced solution for modern security challenges.

Advantages of Heated Bulletproof Glass
🔒 High Safety
Protection against bullets and blast waves thanks to its multilayer structure.
🌫️ Comfort and Visibility
No condensation or frost — improved visibility in all conditions.
⚡ Energy Efficiency
Modern heating systems consume minimal energy.
🛠️ Durability
The combination of strong materials ensures a long service life.
Applications
🔹 Armored vehicles for VIPs, cash-in-transit services, and military use.
🔹 Secured buildings: bank branches, government facilities, embassies.
🔹 Aviation, marine transport, and special-purpose equipment for extreme conditions.
In conclusion, heated bulletproof glass is more than just protection — it’s a high-tech comfort solution that makes life safer and more convenient in any situation.